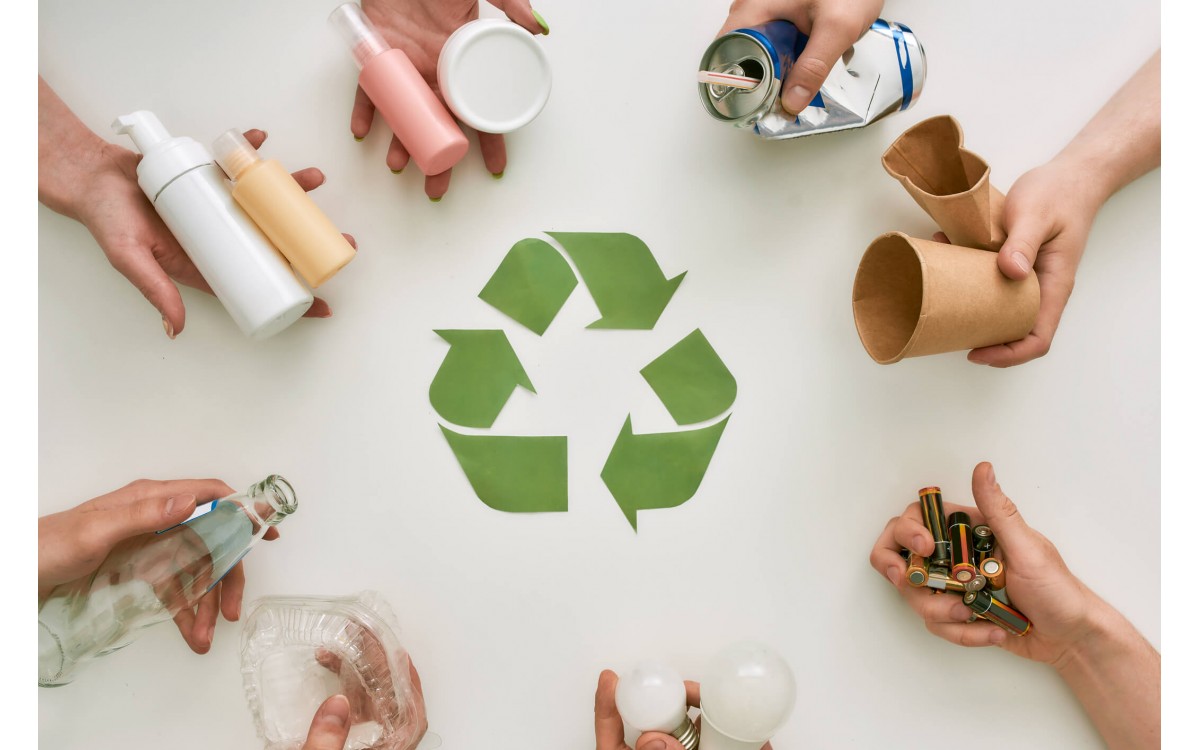
Waste segregation is becoming a good habit in Poland, but sometimes we forget how important it is for the environment. The stakes are not only protecting people and nature from pollution, but also efficient management of resources and energy. In this article, we will remind you what recycling is, what is suitable for recycling and how to practically segregate waste in companies, institutions or in urban spaces.
Recycling - definition
It is a process during which specific waste is transformed into new products. Recycling is part of a much broader phenomenon - recovery. So it's not the same - every recycling is recovery, but not every recovery is recycling. Recovery includes all permitted ways of processing waste, e.g. incineration. As part of recycling, only another product is created, and as part of recovery, energy can also be recovered from waste - either through the aforementioned incineration or by producing alternative fuel from waste.
The most important idea of recycling is to maximize the use of waste with minimal raw material and energy input.
Let's look more closely at what recycling involves. We distinguish 4 basic stages:
- Segregation:
according to the principle of the Uniform Waste Segregation System (JSSO), resources that can be reprocessed are separated from those that can no longer be used. The European Union, to avoid confusion at the selection stage, recommends a 5-bin system. So we collect separately: paper, metals and plastics, glass, biodegradable waste, mixed waste. We can carry out the segregation stage ourselves. Remember that if we declare that we do not segregate waste, an additional fee will be imposed on us. Always accurate information on proper segregation can be found on the website of your municipality.
A full range of bins for internal and external segregation can be found in the category Bins and containers for segregation.
- Shredding:
to facilitate further transport and processing, segregated waste goes to mills equipped with knives and sieves. - Washing:
glass and plastics go to water baths with detergents. Then the waste is centrifuged and dried. - Extrusion:
the heart of the whole process. At this stage, the final product is created, e.g. plastic granules or - in the case of glass - the final product ready for use.
What is subject to recycling?
Let's take a quick look at the 4 most troublesome sections. What can we throw into individual containers to be suitable for recycling later?
- Paper:
newspapers, magazines, notebooks, books, catalogs, leaflets, office/school paper, printed loose sheets, paper packaging, cardboard, corrugated cardboard, paper bags.
Before throwing away, we get rid of all metal and plastic elements! - Metals and plastics:
we often wonder which plastic to recycle? Rightly so - not everyone can go to the yellow container! Among others, containers for paints and varnishes, electronic equipment (including toys), packaging for medicines/medical articles we throw into containers for hazardous waste.
We can throw into the yellow bin: beverage bottles, food product packaging (also canned food cans), multi-material packaging (e.g. milk cartons), cosmetics and cleaning product packaging, caps, bottle caps, jar lids, plastic bags, aluminum foil. - Glass:
bottles and jars for drinks and food (also for vegetable oils), glass cosmetics packaging.
But not : heat-resistant dishes, ceramics, mirrors, candlesticks, eyeglass glass. We throw these into mixed ones. - Biodegradable:
food leftovers, vegetable and fruit waste, tree/shrub branches, mown grass, leaves, flowers, sawdust, untreated wood.
But not : bones and animal droppings, soil, stones, chipboard.
A few tips on how to manage waste consciously can be found in the article "Waste and waste segregation - how to do it and why is it worth it?".


Recycling gives a second life
We use many products every day that were created thanks to good waste segregation. Do you know which ones?
What is made from paper recycling?
Paper has a huge potential! From waste paper, even 5000 different types of products are created, e.g.: egg packaging, coffee filters, napkins, flower pots, paper for books/newspapers/notebooks, ear sticks, bandages, toilet paper, and even car insulation and banknotes.
Metal recycling - what is made?
Pipes, cables, insulation, sometimes even artistic jewelry. Aluminum is an important raw material. Recycling allows in its case to save up to 95% of energy compared to the production of new aluminum from ore. What is made from can recycling? Not only new packaging. The recovered material is used by the automotive and aviation industries to produce machine parts.
What is made from glass recycling?
Glass is a very grateful material. We can recycle it almost indefinitely, without losing the properties of the raw material. From used glass, for example, new bottles, glasses, jars, tiles, kitchen countertops, wall insulation are created.
Plastic recycling - what is made?
We are surrounded by many products made from recycled plastic every day. These include pens, bottles, packaging, sports shoes, tents, garden furniture, specialist clothing. One polar fleece can be produced from 35 PET bottles!
Segregate wisely - these 3 rules will make your life easier
- Don't drown in cans and bottles: use a small home can and bottle crusher that you can hang on the wall. More models of crushers of different sizes can be found in this section Crushers for bottles and cans.
- Don't waste water and time: we often wonder whether to wash plastics for segregation. No! You don't have to wash either plastic or glass containers (even with oil). It is important to empty them of food residues.
- Dirty paper... is not paper: all greasy, dirty cartons (e.g. pizza), disposable dishes, tissues, paper towels without hesitation throw into mixed ones.
Recycling signs and their meaning
What recycling signs can we most often encounter?
- Packaging made of recyclable materials
- The number in the recycling symbol and the abbreviation under the symbol indicate exactly what material the product is made of:
- numbers 1–7 and 9 denote plastics (e.g. 01 PET - polyethylene terephthalate, 03 PVC - polyvinyl chloride, 04 LDPE - low density polyethylene, 05 PP - polypropylene)
- numbers 08, 10–19 denote batteries
- numbers 20–23 papers
- numbers 40–41 metals
- numbers 50–62 biomass
- numbers 70–79 glass
- numbers 81–98 composites
- Biodegradable packaging, will decompose during composting
- Package for reuse
- The product must not be thrown into ordinary containers. It applies, among others, to electronic waste
Convenient waste segregation - opt for practical bins
Effective waste selection must be convenient for users. How to choose containers?
- Consider whether you are looking for aesthetic bins that are to stand inside the building (check the category Internal segregation bins) or spacious, strong containers for the backyard (browse the category Waste containers).
- How many segregation compartments do users need the most? Not everywhere do you need bins with 5 sections! The most popular are 2-compartment stations and 3-compartment ones. You can decide what fractions you want. At the ordering stage, you choose inscriptions in segregation colors.
- What capacity will pass the test in this particular place? The offer includes handy sets for schools or offices from 25 L, e.g. Sortbucket 4 x 25L segregation bin.
- Maybe only mobile bag stands will suffice? They are used during outdoor events, on recreational plots or gardens. They fit bags of different capacities. A strong rim and stable construction ensure hygienic, safe use of bins.
Looking for specific inspirations? Check out the top 10 segregation sets for your company.
- Do you want to encourage children to segregate waste? If we talk about recycling, the definition for children must go hand in hand with fun and positive associations. We have designated these containers for children for such a special mission - their colors and shapes will certainly intrigue the youngest.
Why is recycling important?
For at least three reasons. First of all - broadly understood economy. Recycling allows cheaper production of new products, development of a sector that guarantees new jobs. Secondly - ecology. How does recycling affect the environment? Thanks to it, we take care of nature so that it does not suffer from the decomposition of toxic substances, we reduce the number of landfills, we save resources, the resources of which are limited after all. Finally, the ethical aspect is invaluable - recycling teaches respect for objects and leads to an important reflection that "old" does not mean "useless".









 Waste Containers
Waste Containers Waste Bins
Waste Bins Street And Park Waste Bins
Street And Park Waste Bins Sand And Salt Containers
Sand And Salt Containers Hazardous Waste Containers
Hazardous Waste Containers House And Garden
House And Garden Park Benches
Park Benches







